AC 自动机
AC 自动机 = \text{trie} + \text{kmp} 的思想
AC 自动机
问题:给定 n 个模式串和一个文本串,问有多少个模式串出现在文本串中
跑 n 遍 \text{kmp} ?若数据毒瘤会超时
于是一些珂学家们发明了 AC 自动机
fail
假设模式串分别是 he she her shy say
建出 \text{trie} 树
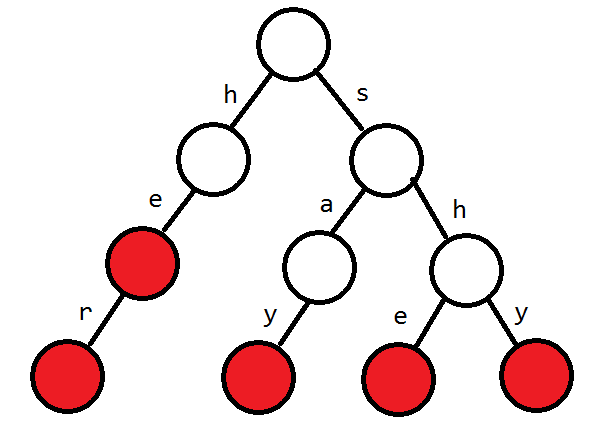
暴力匹配效率不高,考虑用 \text{kmp} 的 next 思想,在 \text{trie} 上建一个 fail
设当前串 S 以 u 结尾,则 fail_u 指向
能与 S 后缀匹配的)最长的) \text{trie} 的前缀所在的)节点
这着实有点绕,可以康康图
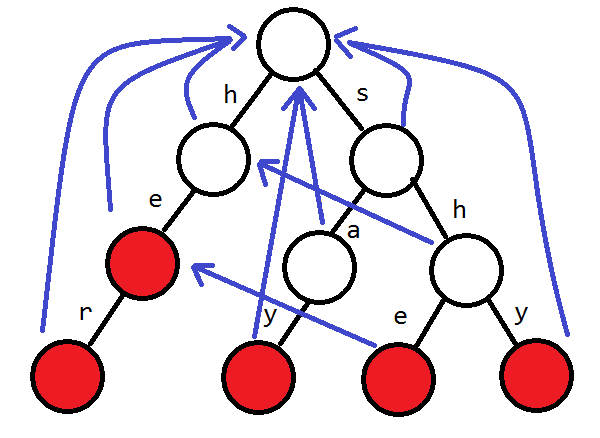
如图,能与 she 的后缀匹配的 \text{trie} 的前缀,只有 he
如何构建
考虑 bfs ,对于当前点 u 存在的儿子 ch_{u,i}
从 u 开始往上跳 fail,直到一个点 v 也有 ch_{v,i} ,那么 ch_{u,i} 的 fail 指向 ch_{v,i}
特别的,如果没有符合条件的 v ,那么 fail 指向根
同时第二层的 fail 都指向跟
inline void gfail() {
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
if(ch[0][i])q[++tl]=ch[0][i];
register int u;
while(hd<tl) {
u=q[++hd];
for(int i=0,v;i<26;i++) {
if(ch[u][i]) {
v=fail[u];
while(!ch[v][i] && v)v=fail[v];
fail[ch[u][i]]=ch[v][i];
q[++tl]=ch[u][i];
}
}
}
}
查询
如何查询文本串 s 呢
指针 u 从根开始,将每个字母送入自动机
若不存在 ch_{u,c} ,则跳 fail 找到一个存在的 ch_{v,c}
然后沿着从 fail 到根的路径统计个数,
注意不要重复
inline int ask(int le) {
register int u=0,ans=0;
for(int i=1,v;i<=le;i++) {
v=s[i]-'a';
while(!ch[u][v] && u)u=fail[u];
u=ch[u][v];
for(int j=u;j && flg[j];j=fail[j])
ans+=flg[j],flg[j]=0;
}
return ans;
}
trie 图
发现如果当前节点没有对应的子节点,那么就需要沿着 fail 向上走,会浪费时间
考虑在建立 fail 时补全 \text{trie} 树,形成 \text{trie} 图
若 u 不存在儿子 i ,则将儿子 i 指向 fail_u 儿子 i
否则直接将儿子的 fail 指向 fail_u 的儿子 i
inline void gfail() {
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
if(ch[0][i])q[++tl]=ch[0][i];
register int u;
while(hd<tl) {
u=q[++hd];
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
if(ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]]=ch[fail[u]][i];
q[++tl]=ch[u][i];
} else ch[u][i]=ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
匹配完后的查询也不需要跳 fail 了
inline int ask(int le) {
register int u=0,ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=le;i++) {
u=ch[u][s[i]-'a'];
for(int j=u;j && flg[j];j=fail[j])
ans+=flg[j],flg[j]=0;
}
return ans;
}
Code
例:模板
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1000005;
int n,ch[N][26],fail[N],flg[N],tot,hd,tl,q[N];
char s[N];
inline void ins(int le) {
register int u=0;
for(int i=1,v;i<=le;i++) {
v=s[i]-'a';
if(!ch[u][v])ch[u][v]=++tot;
u=ch[u][v];
}
flg[u]++;
}
inline void gfail() {
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
if(ch[0][i])q[++tl]=ch[0][i];
register int u;
while(hd<tl) {
u=q[++hd];
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
if(ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]]=ch[fail[u]][i];
q[++tl]=ch[u][i];
} else ch[u][i]=ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
inline int ask(int le) {
register int u=0,ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=le;i++) {
u=ch[u][s[i]-'a'];
for(int j=u;j && flg[j];j=fail[j])
ans+=flg[j],flg[j]=0;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
scanf("%s",s+1);
ins(strlen(s+1));
}
gfail();
scanf("%s",s+1);
printf("%d",ask(strlen(s+1)));
}
例:查询出现个数,一样的题
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1000005;
int n,ch[N][26],mx,ans[N],fail[N],flg[N],tot,hd,tl,q[N];
char s[N],st[200][200];
inline void ins(int le,int id) {
register int u=0;
for(int i=1,v;i<=le;i++) {
v=st[id][i]-'a';
if(!ch[u][v])ch[u][v]=++tot;
u=ch[u][v];
}
flg[u]=id;
}
inline void gfail() {
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
if(ch[0][i])q[++tl]=ch[0][i];
register int u;
while(hd<tl) {
u=q[++hd];
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
if(ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]]=ch[fail[u]][i];
q[++tl]=ch[u][i];
} else ch[u][i]=ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
inline void ask(int le) {
register int u=0;
for(int i=1;i<=le;i++) {
u=ch[u][s[i]-'a'];
for(int j=u;j;j=fail[j])
ans[flg[j]]++;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n) {
memset(ch,0,sizeof(ch));
memset(flg,0,sizeof(flg));
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
scanf("%s",st[i]+1);
ins(strlen(st[i]+1),i);
}
gfail();
scanf("%s",s+1);
ask(strlen(s+1));
mx=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)mx=max(mx,ans[i]);
printf("%d\n",mx);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(ans[i]==mx)printf("%s\n",st[i]+1);
scanf("%d",&n);
}
}
Fail 树
用途:统计模式串出现的个数
和加强版很想?可是暴力跳巨慢?
想想匹配的过程,从头开始跳 fail ,期间到的每个点都是一个出现的串
既然可以一个一个顺着跳,同理从模式串结尾往上跳到的节点个数就是该串出现的次数
于是可以只留下反着的 fail 边,形成 fail 树
只要将属于文本串的节点标为 1 ,那么节点 u 的子树和就是 u 出现的次数
子树和可以用 \text{dfs} 序+树状数组,复杂度下降许多
例:几乎一样的题
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2000005;
int n,len,ch[N][26],fail[N],flg[N],tot,hd,tl,q[N],sz[N],tr[N];
char s[N];
int lst[N],nxt[N],to[N],cnt,dff,dfn[N];
inline void Ae(int fr,int go) {
to[++cnt]=go,nxt[cnt]=lst[fr],lst[fr]=cnt;
}
inline void ins(int le,int id) {
register int u=0;
for(int i=1,v;i<=le;i++) {
v=s[i]-'a';
if(!ch[u][v])ch[u][v]=++tot;
u=ch[u][v];
}
flg[id]=u;
}
inline void gfail() {
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
if(ch[0][i])q[++tl]=ch[0][i];
register int u;
while(hd<tl) {
u=q[++hd];
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
if(ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]]=ch[fail[u]][i];
q[++tl]=ch[u][i];
} else ch[u][i]=ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)
Ae(fail[i],i);
}
void dfs(int u) {
dfn[u]=++dff,sz[u]=1;
for(int i=lst[u],v;i;i=nxt[i])
dfs(v=to[i]),sz[u]+=sz[v];
}
inline void add(int p,int v) { for(;p<=dff;p+=p&-p)tr[p]+=v; }
inline int ask(int p) { register int s=0; for(;p;p-=p&-p)s+=tr[p]; return s; }
inline int tree(int u) { return ask(dfn[u]+sz[u]-1)-ask(dfn[u]-1); }
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
scanf("%s",s+1);
ins(strlen(s+1),i);
}
gfail(),scanf("%s",s+1),len=strlen(s+1);
dfs(0);
for(int i=1,u=0;i<=len;i++)u=ch[u][s[i]-'a'],add(dfn[u],1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)printf("%d\n",tree(flg[i]));
}
一些灵活应用
可以通过反向 \text{dfs} 序实现 O(n) 求出答案
把队列反向枚举,然后把 fail_u 的答案加上 u 的答案
因为 \text{bfs} 满足深度的递增
// https://gmoj.net/senior/#main/show/4328
// https://gmoj.net/senior/#main/code/808016
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2000005;
int n,len,ch[N][26],fail[N],flg[N],tot,hd,tl,q[N],sz[N];
char s[N];
inline void ins(int le,int id) {
register int u=0;
for(int i=1,v;i<=le;i++) {
v=s[i]-'a';
if(!ch[u][v])ch[u][v]=++tot;
u=ch[u][v];
}
flg[id]=u;
}
inline void gfail() {
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
if(ch[0][i])q[++tl]=ch[0][i];
register int u;
while(hd<tl) {
u=q[++hd];
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
if(ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]]=ch[fail[u]][i];
q[++tl]=ch[u][i];
} else ch[u][i]=ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
scanf("%s",s+1);
ins(strlen(s+1),i);
}
gfail(),scanf("%s",s+1),len=strlen(s+1);
for(int i=1,u=0;i<=len;i++)u=ch[u][s[i]-'a'],sz[u]++;
for(int i=tl;i;i--)sz[fail[q[i]]]+=sz[q[i]];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)printf("%d\n",sz[flg[i]]);
}
AC 自动机上 dp
不知道哪一位神仙发明的东西
主要和字符串的包含关系有关,一般的状态至少两维, f_{i,j} 表示第 i 步在自动机上节点 j
第一维在一些题目里可以省略。
Wireless Password
以 Wireless Password 为例,题目求包含 k 个给定串的长度为 n 的字符串个数。
建出自动机,自动机上节点 j 包含的串就是 fail 链上的串。
又因为 k 很小,可以考虑状压,记 flg_j 为节点 j 包含的串的集合
设 f_{i,j,k} ,k 为当前包含的字符串集合。则 f_{i+1,v,k\cup flg_v}\leftarrow f_{i,j,k} 。其中 v 为节点 j 的儿子
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
typedef long double LD;
typedef long long LL;
typedef double db;
const LL P = 20090717;
int n, m, K, ch[105][26], fail[105], flg[105], tot, f[30][105][1100];
char a[105];
inline void ins(int le, int pos) {
register int u = 0;
for (int i = 1, s; i <= le; i++) {
s = a[i] - 'a';
if (!ch[u][s]) {
ch[u][s] = ++tot;
memset(ch[tot], 0, sizeof(ch[tot]));
}
u = ch[u][s];
}
flg[u] = 1 << (pos - 1);
}
queue<int> Q;
inline void gf() {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (ch[0][i]) Q.push(ch[0][i]);
for (int u; !Q.empty(); ) {
u = Q.front(), Q.pop();
flg[u] |= flg[fail[u]];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
Q.push(ch[u][i]);
} else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &K), n) {
memset(ch[0], 0, sizeof(ch[0]));
memset(fail, 0, sizeof(fail));
memset(flg, 0, sizeof(flg));
tot = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%s", a + 1);
ins(strlen(a + 1), i);
}
gf();
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
f[0][0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= tot; j++)
for (int s = 0; s < (1 << m); s++) {
if (!f[i][j][s]) continue;
for (int k = 0, v; k < 26; k++) {
v = ch[j][k];
(f[i + 1][v][s | flg[v]] += f[i][j][s]) %= P;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int s = 0, t, l; s < (1 << m); s++) {
for (l = 0, t = s; t; t -= t & -t, l++);
if (l >= K) {
for (int j = 0; j <= tot; j++)
(ans += f[n][j][s]) %= P;
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
DNA Sequence
求长度为 n 的不包含给定串的字符串个数,n\le 2\times 10^9
同理,建自动机,如果 j 的 fail 链上有字符串,则点 j 不能访问。
f_{i+1,v}\leftarrow f_{i,j} ,需要满足, v 能访问。
n 有点大,但其实容易想出矩阵优化,从 0 出发走 n 步的方案,将一步走到的点赋值,最终 \sum a_{0,i}
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
typedef long double LD;
typedef long long LL;
typedef double db;
const int P = 100000;
inline int id(char c) {
if (c == 'A') return 0;
if (c == 'C') return 1;
if (c == 'T') return 2;
return 3;
}
int n, K, ch[105][5], fail[105], flg[105], tot;
char a[15];
inline void ins(int le) {
register int u = 0;
for (int i = 1, s; i <= le; i++) {
s = id(a[i]);
if (!ch[u][s]) ch[u][s] = ++tot;
u = ch[u][s];
}
flg[u] = 1;
}
struct mat {
int a[105][105];
mat() { memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)); }
mat operator * (mat b) {
mat c;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= tot; j++)
for (int k = 0; k <= tot; k++)
(c.a[i][j] += 1ll * a[i][k] * b.a[k][j] % P) %= P;
return c;
}
} ;
queue<int> Q;
inline void GF() {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
if (ch[0][i]) Q.push(ch[0][i]);
for (int u; !Q.empty(); ) {
u = Q.front(), Q.pop();
flg[u] |= flg[fail[u]];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
Q.push(ch[u][i]);
} else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &K) != EOF) {
tot = 0;
memset(fail, 0, sizeof(fail));
memset(ch, 0, sizeof(ch));
memset(flg, 0, sizeof(flg));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%s", a + 1);
ins(strlen(a + 1));
}
GF();
mat o, res;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
if (!flg[ch[i][j]]) o.a[i][ch[i][j]]++;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++) res.a[i][i] = 1;
for (; K; K >>= 1, o = o * o)
if (K & 1) res = res * o;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++) (ans += res.a[0][i]) %= P;
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
考研路茫茫——单词情结
求长度不超过 n 的包含给定串的字符串个数,可以用总数减去不包含的个数。
构造矩阵的方法同上,区别是要求 A+A^2+\cdots+A^n ,这是矩阵的经典运用,分治 + 快速幂解决。
同理,总数为 26+26^2+\cdots+26^n ,求法一样。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
typedef long double LD;
typedef long long LL;
typedef double db;
int n, L, ch[35][26], fail[35], vis[35], tot;
char a[10];
struct mat {
uLL a[35][35];
mat() { memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)); }
mat operator * (mat b) {
mat c;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= tot; j++)
for (int k = 0; k <= tot; k++)
c.a[i][j] += a[i][k] * b.a[k][j];
return c;
}
mat operator + (mat b) {
mat c;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= tot; j++)
c.a[i][j] = a[i][j] + b.a[i][j];
return c;
}
};
inline void ins(int le) {
register int u = 0;
for (int i = 1, s; i <= le; i++) {
s = a[i] - 'a';
if (!ch[u][s]) ch[u][s] = ++tot;
u = ch[u][s];
}
vis[u] = 1;
}
queue<int> Q;
inline void gf() {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (ch[0][i]) Q.push(ch[0][i]);
for (int u; !Q.empty(); ) {
u = Q.front(), Q.pop();
vis[u] |= vis[fail[u]];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
Q.push(ch[u][i]);
} else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
mat Pow(mat x, int y) {
mat res;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++) res.a[i][i] = 1;
for (; y; y >>= 1, x = x * x)
if (y & 1) res = res * x;
return res;
}
mat cal(mat a, int n) {
if (n == 1) return a;
mat res = cal(a, n >> 1);
if (n & 1) {
mat t = Pow(a, n / 2 + 1);
res = (res + (t * res)) + t;
} else {
mat t = Pow(a, n / 2);
res = res + (t * res);
}
return res;
}
uLL Pow(uLL x, int y) {
uLL res = 1;
for (; y; y >>= 1, x = x * x)
if (y & 1) res = res * x;
return res;
}
uLL cal(uLL a, int n) {
if (n == 1) return a;
uLL res = cal(a, n >> 1);
if (n & 1) {
uLL t = Pow(a, n / 2 + 1);
res = res + (t * res) + t;
} else {
uLL t = Pow(a, n / 2);
res = res + (t * res);
}
return res;
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &L) != EOF) {
tot = 0;
memset(ch, 0, sizeof(ch));
memset(fail, 0, sizeof(fail));
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%s", a + 1);
ins(strlen(a + 1));
}
gf();
mat st;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++)
if (!vis[ch[i][j]]) st.a[i][ch[i][j]]++;
// for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++, puts(""))
// for (int j = 0; j <= tot; j++) cout << st.a[i][j] << ' ';
uLL tmp = cal(26, L);
mat res = cal(st, L);
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
tmp -= res.a[0][i];
printf("%llu\n", tmp);
}
}
Lost's revenge
给定 n 个模式串,要求文本串重组后包含最多模式串个数。
字符串只包含 A,T,G,C ,可以用四维状态表示一个字符串。
其实没有必要,文本串长度最多为 40,
用一个类似哈希的数组 h_{i,j,k,l} 表示 i 个 A ,j 个 C ,k 个 G ,l 个 T 的状态编号。
没有必要记录长度, f_{j,s} 表示在 j 号点,状态为 s ,s 最多为 40
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
typedef long double LD;
typedef long long LL;
typedef double db;
int n, Tk, tot, ch[505][4], fail[505], cnt[505], o[4], h[45][45][45][45], f[505][15000];
char a[55];
inline int id(char c) {
if (c == 'A') return 0;
if (c == 'C') return 1;
if (c == 'G') return 2;
return 3;
}
inline void ins(int le) {
register int u = 0;
for (int i = 1, s; i <= le; i++) {
s = id(a[i]);
if (!ch[u][s]) ch[u][s] = ++tot;
u = ch[u][s];
}
++cnt[u];
}
queue<int> Q;
inline void gf() {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
if (ch[0][i]) Q.push(ch[0][i]);
for (int u; !Q.empty(); ) {
u = Q.front(), Q.pop();
cnt[u] += cnt[fail[u]];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (ch[u][i]) {
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
Q.push(ch[u][i]);
} else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d", &n), n) {
memset(ch, 0, sizeof(ch));
memset(fail, 0, sizeof(fail));
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));
tot = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%s", a + 1);
ins(strlen(a + 1));
}
gf();
scanf("%s", a + 1);
memset(o, 0, sizeof(o));
int le = strlen(a + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= le; i++)
o[id(a[i])]++;
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= o[0]; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= o[1]; j++)
for (int k = 0; k <= o[2]; k++)
for (int l = 0; l <= o[3]; l++)
h[i][j][k][l] = pos++;
memset(f, -1, sizeof(f));
f[0][0] = 0;
for (int A = 0; A <= o[0]; A++)
for (int C = 0; C <= o[1]; C++)
for (int G = 0; G <= o[2]; G++)
for (int T = 0; T <= o[3]; T++) {
int s = h[A][C][G][T];
int nw[4] = { A, C, G, T };
for (int j = 0; j <= tot; j++)
for (int k = 0, v, ns; k < 4; k++) {
if (nw[k] == o[k] || f[j][s] == -1) continue;
nw[k]++;
v = ch[j][k], ns = h[nw[0]][nw[1]][nw[2]][nw[3]];
f[v][ns] = max(f[v][ns], f[j][s] + cnt[v]);
nw[k]--;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= tot; i++)
ans = max(ans, f[i][pos - 1]);
printf("Case %d: %d\n", ++Tk, ans);
}
}
总结
AC 自动机是一个有力的工具,应在做题中深入理解
本文作者:小蒟蒻laf
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/KonjakLAF/p/14860486.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。



【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,携手博客园推出1Panel与Halo联合会员
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步